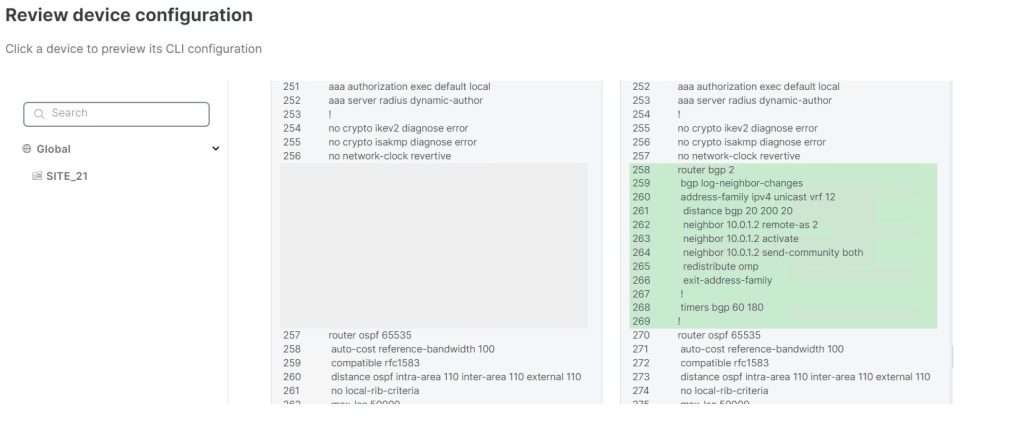
Traditionally AMP is able to detect for any malicious activity by using signature based detection, what this means is AMP will download the database which then uses this to compare with any well known malicious files against the database. This allows Organisations to protect against malware infection. This solution worked against the common threats, however it’s unable to detect any new threats that have been flagged as malicious yet.
With Next Generation AMP and tied to SASE is that regardless of where the network/user is, it will be protected. This is due to the fact SASE model means all security services are in the cloud without physical hardware limitations. So you can incorporate flexibility and scalability.
Another advantage is that should there be an incident, using SASE would allow other services to mitigate or protect the network without delay. An example could be using IPS in conjunction with AMP or SWG .
Alerts and logging is also centralised without the need to go through different appliances for logs.
Behavioural Detection/NG-AMP
Instead of relying on traditional signature based detection, behavioural detection essentially looks at the files or applications for any suspicious activity. An example could be a file attempting to change the registry of the OS. Another example could be attempting to use tools to hide any malware. All this is done with the help of AI and ML.
Compared to signature based detection, it is able to detect zero day threats.
One thing to be aware of is using this technique because it will be resource intensive as well as false positives could occur.
Ideally if possible, maybe using both techniques would give organisations the best of both worlds!
I will lab up Cisco’s built in Security for Catalyst SD-WAN with demonstration for my next post!
I hope this helps! 😁
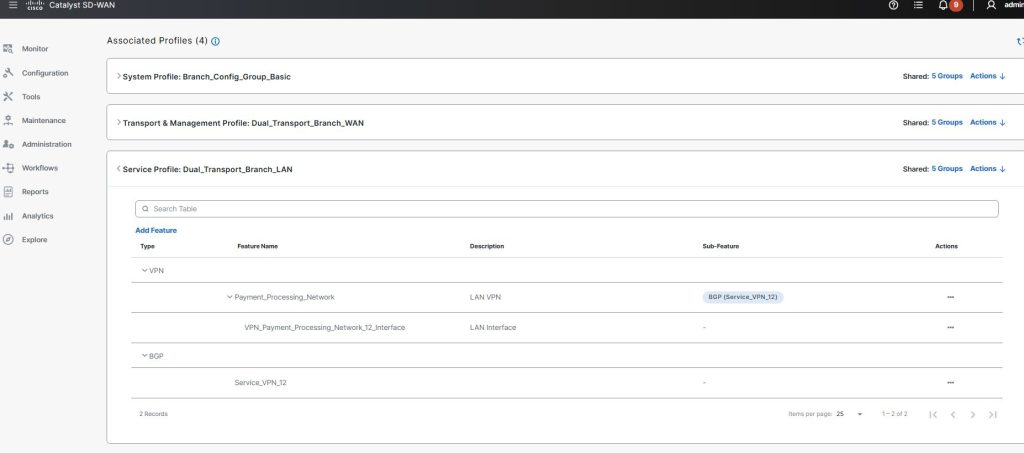
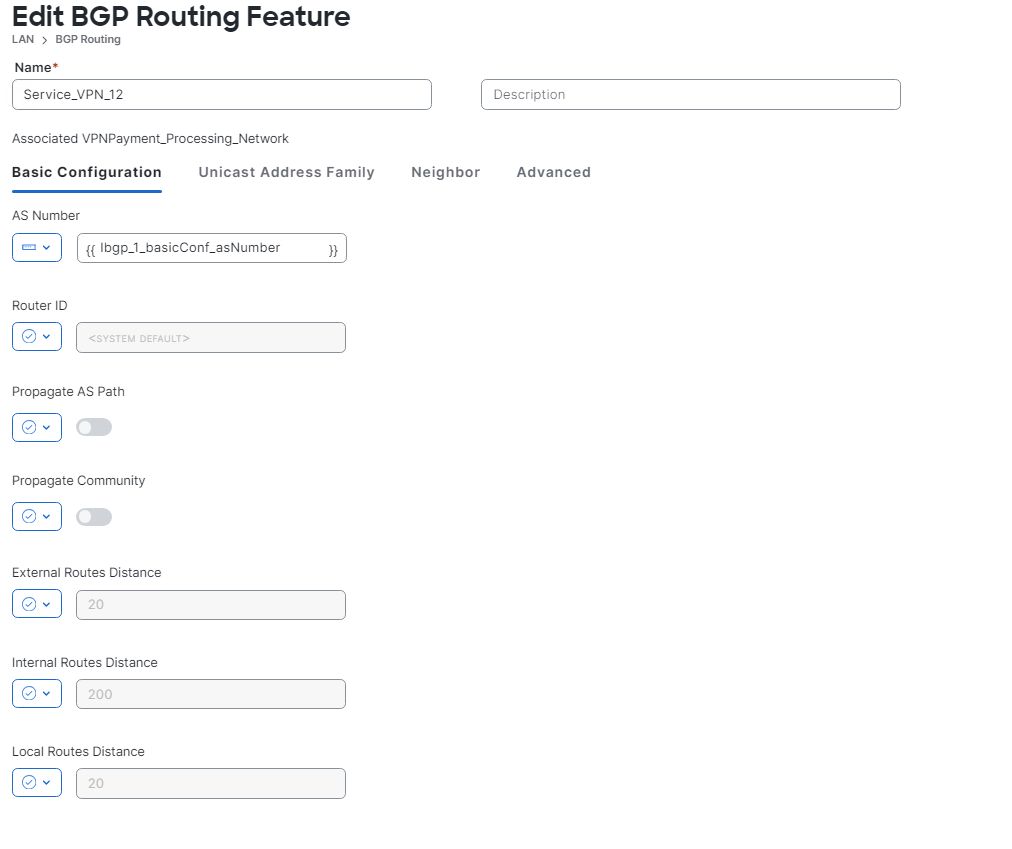
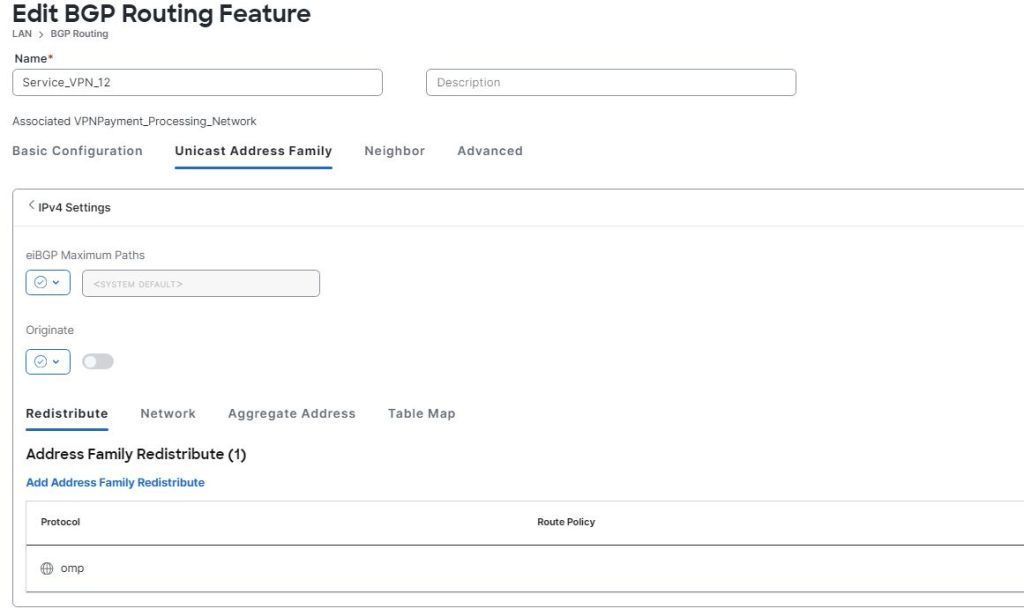
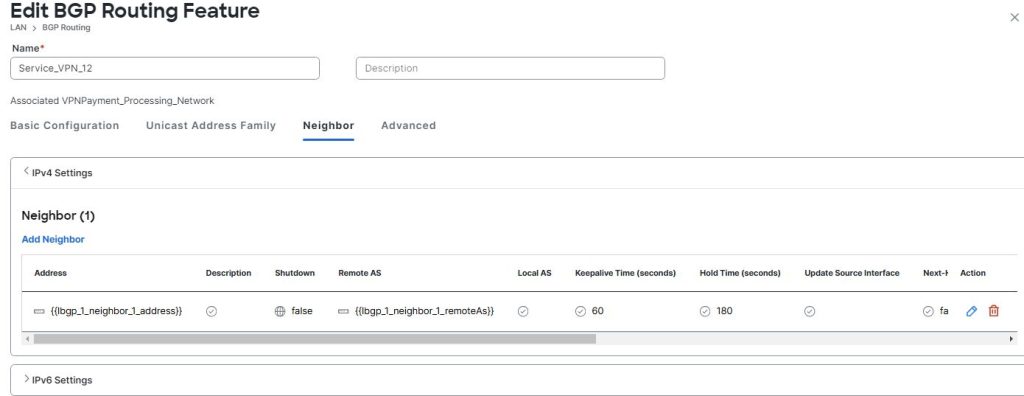
I have included a link in how to configure AMP in Cisco SD-WAN.
http://jaychou.co.uk/?p=1264