AppQoE’s main goal is to improve application Quality of Experience.
AppQoE Features in SD-WAN
BFD
BFD is used for path liveliness and to measure the quality of the link. Whether the link is up/down, loss/latency/jitter
BFD runs between the WAN Edges as well as the Edge Cloud routers.
- Within IPSec tunnels
- Echo mode only
- As soon as IPsec tunnel is stablished BFD will be activated
- There is NO option to disable this
BFD uses Hello intervals, poll interval and multiplier for detection.
Application Aware Routing/Enhanced Application Aware Routing
I have already written a Blog about EAAR (http://jaychou.co.uk/?p=613) – This section is based on standard AAR.
A better example to understand AAR is having a scenario where there are multiple Transports such as Biz-Internet, Internet and LTE. Should there be an issue with one of the Transports which will impact the user experience. With AAR, you create a threshold for a specific Application so should the transport not meet SLA then it will switch to another Transport (fastest is 10minutes unless using EAAR which is 10s).
AAR is measured against Latency/Jitter/Loss, when the user configures the Application Aware Routing Policy then you can set the threshold before the transport switches over. This ensures the SLA is compliant through the SD-WAN fabric.
BFD is used for AAR, which has two timers:
- BFD timer on Transport Tunnels, this is used to define the BFD frequency – such as BFD colour, hello-interval in milliseconds and the multipler in terms of frequency it happens.
- BFD timer for AAR which defines often BFD polls all data plane tunnel stratistics and is used to collect packet latency, loss, and jitter.
Forward Error Correction (FEC)
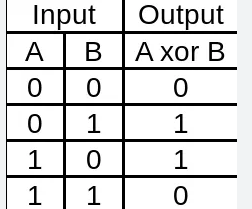
FEC uses the XOR cipher. If the Cipher is the same then no change has been made. An example of XOR operation below:
This helps to understand how FEC is operated, XOR allows FEC to create a parity packet which then reconstructs the lost packet.
FEC helps the following :
- Protects against packet loss
- Operates per-tunnel
- Supports multiple transports
- Can be invoked as and when
- Applied within the Data Policy
FEC can only reconstruct 1 packet out of 4.
Packet Duplication
As the name suggests, this allows duplcating packets for critical traffic/application such as Credit or ATM transactions and sending the duplicated path over a second path.
This can work when there is little or limited of Critical traffic compared to the capacity of the network. If there is multiple circuits then SD-WAN will choose the best transport. Best as in the least amount of packet loss to replicate the packets to.
When transferring, duplicate the packets of the primary tunnel and send simultanousely, the secondary/duplicated tunnel is chosen based on MTU. Duplication happens only if the secondary tunnel MTU is greater or equal to that of first to avoid fragmentation. When the receiving router receives the first packet to the LAN whether it is duplicate or original it will drop the other one.
QoS
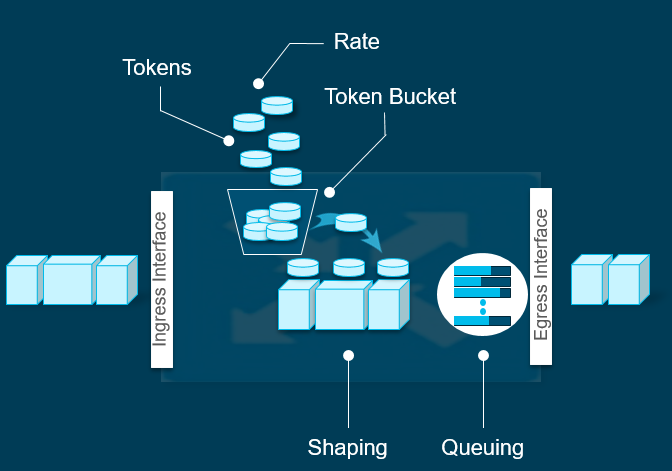
Queuing
Is used when Shaping is being utilised. This allows the packets to sit in a queue waiting to be sent in the egress interface. Uses Weighted Round-Robin, when the queue gets dropped it uses Random Early Discard.
Shaping
Is used when you do not want to drop the packet if there is a queue and exceeded the configured Shaper rate. Essentially if there are no more tokens in the bucket it will be placed in a queue. The queued packets will operate in Weighted Round-Robin. This is not supported on Sub-interfaces.
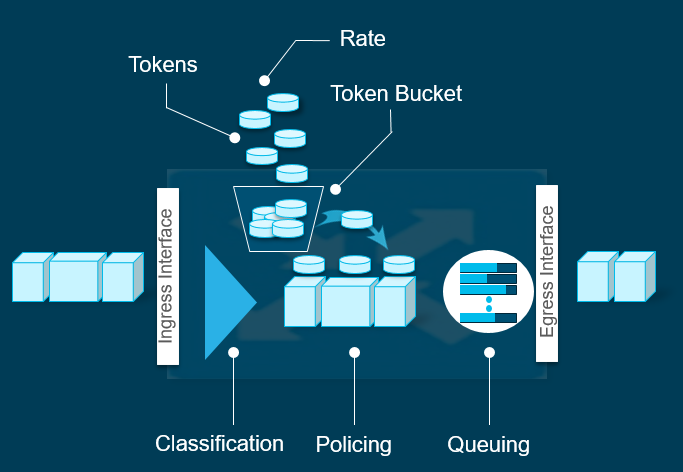
Policing
Is used if you want to completely drop the traffic if does not conform the policer rate.
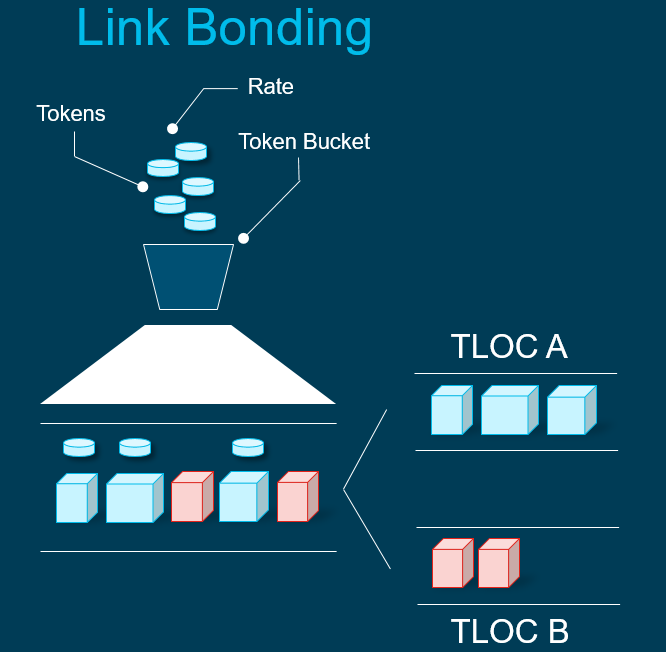
Link Bonding
You can bond both transport links together – this essentially means it will be per packet load sharing, with the receiving host ordering the packets if packets are being send out of order.
None-conforming traffic will spill over to a different circuit.
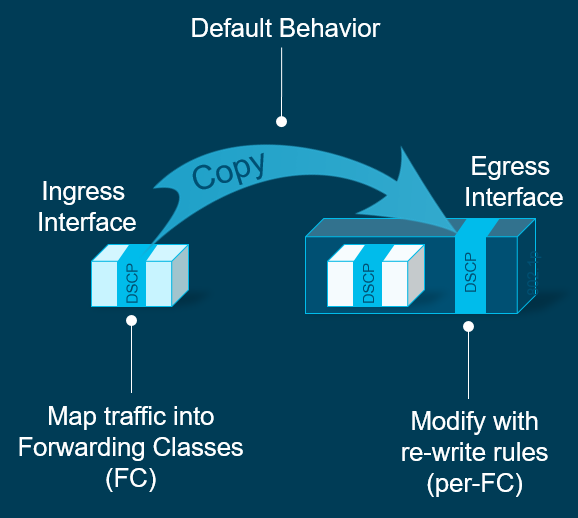
DSCP Marking an Remarking
DSCP operates on Layer 3, so as a packet is being mapped into a forwarding class, you can modify this to another DSCP rule.
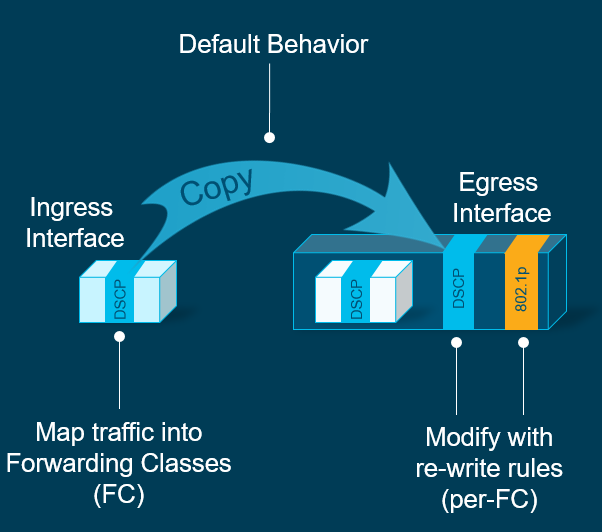
COS (802.1p) Marking and Re-marking
You can remark COS (Layer 2) frames.
Path Quality and Liveliness Detection
Each WAN Edge router sends BFD Hello packets for path quality and liveliness detection, the packets will be echoed back by the receiving router. Using Hello interval and multiplier will determine how many BFD packets need to be lost in order to declare whether the IPsec tunnel is down.
The number of hello intervals that fit inside the Poll interval determins the number of BFD packets considered for establising poll interval average path quality.
The App Route multuplier determines the number of poll intervals for establishing the ocerall average path quality.
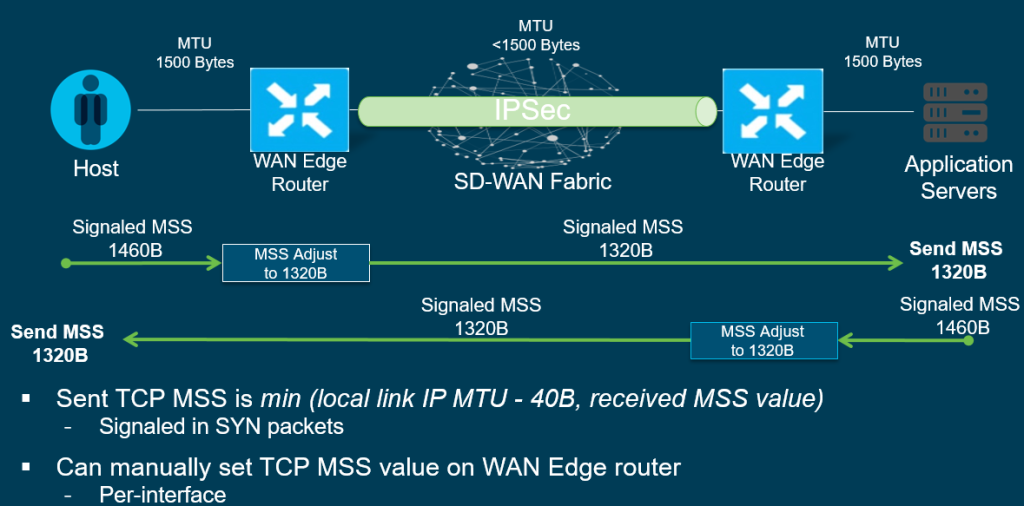
TCP MSS Adjust
This is used to help the need in fragmentation of packets, Routers on the WAN edge will signal the appropriate MTU based on the host/application on the LAN. This in turn will be forwarded to the receiving router in terms of the appropriate MTU it needs to be.
Per-Tunnel QoS support on SD-WAN
This allows the site to dynamically adjust the sending rate of its traffic to acomodate lower bandwidth circuits at remote sites.
Cloud onRamp for SaaS
Cloud on Ramp allows quality probing towards popular SaaS Application, the WAN Edge router chooses the best porforming path towards the popular Saas Applications.
CoR works by using the following 3 components:
- DNS Resolution
- Performance Visibility
- Path Selection
An example is if you had two DIA transports to the SaaS application, CoR monitors the edge to the SaaS application. This in turn then picks the best porforming metrics such as loss and delay.
Perfomance Visiibilty works by the WAN edge reuesting DNS in VPN0 and sends a DNS reuest for the pre-configured SaaS application.
DNS requests are duplicated and sent to all transports to get the application server address.
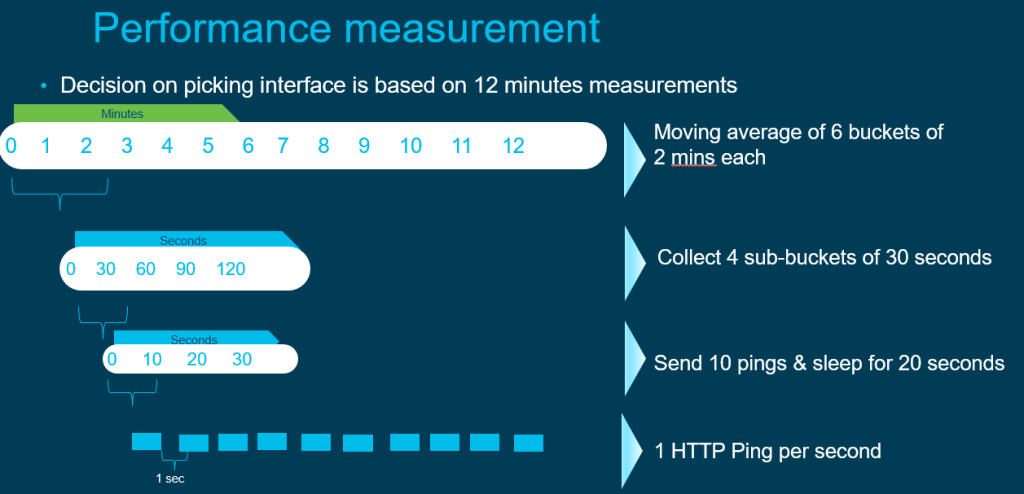
HTTP pings are sent to the application such as SalesForce servers on both the DIA links for performance measurements.
The results and score is measured from 0-10 with 10 being the best.
0-5 RED
5-8 Yellow
8-10 Green
TCP Optimisation
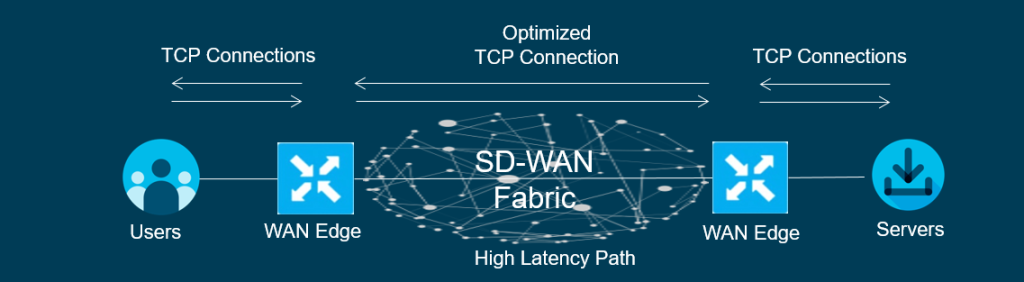
TCP optimisation fine tunes the processing of TCP traffic which in turn decreases the round-trip latency to improve throughput.
An example is if you are using a high latency link like a satelite transport attempting to connect to a SaaS based or Server, the TCP handshake is formed from Client to the Router. This TCP connection will be terminated and in turn the router will then form another TCP handshake with the remote router. This TCP handshake from WAN Edge to WAN Edge will be cached. The remote router will form a TCP handshake with the Server.
SD-AVC – Advanced Visibilility Control
Essentially using NBAR2 to classify and regonise applications, it uses DPI plus different techniques such as:
- DNS Snooping
- ML
- Behavioural classification
- Learning of main services and servers
- Customisations