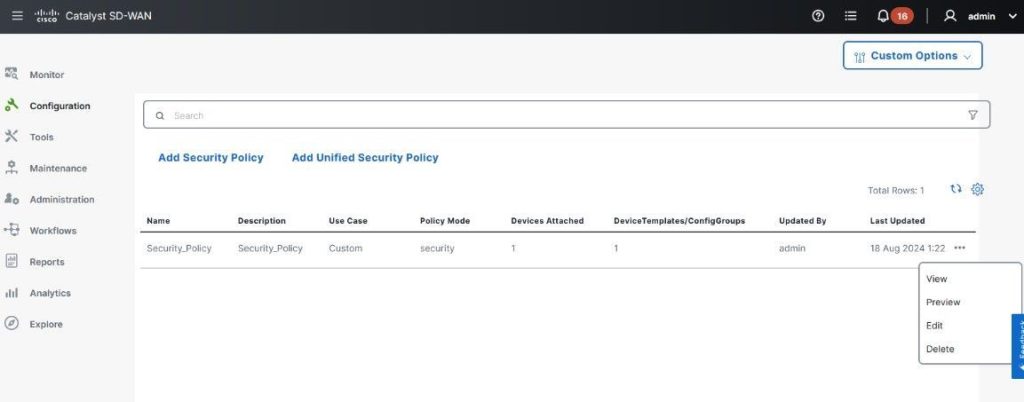
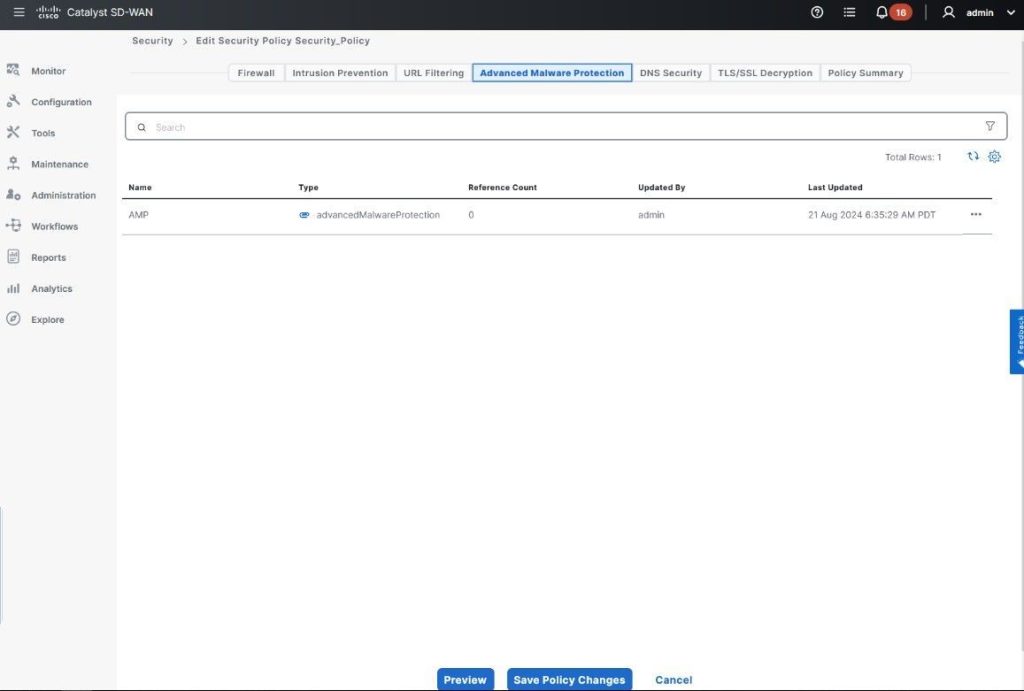
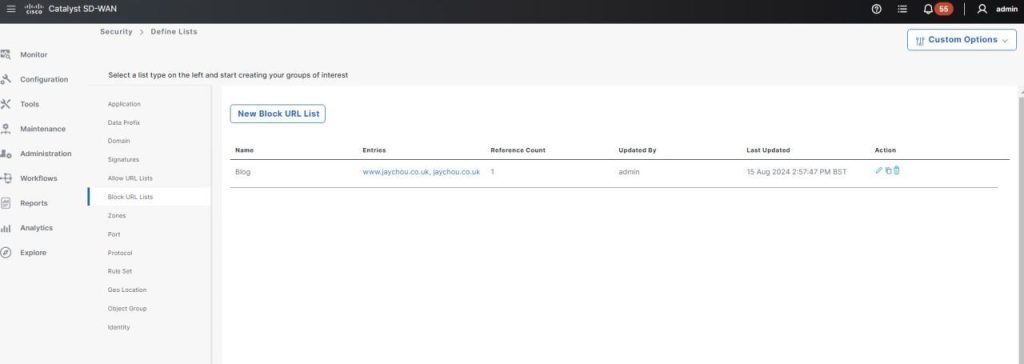
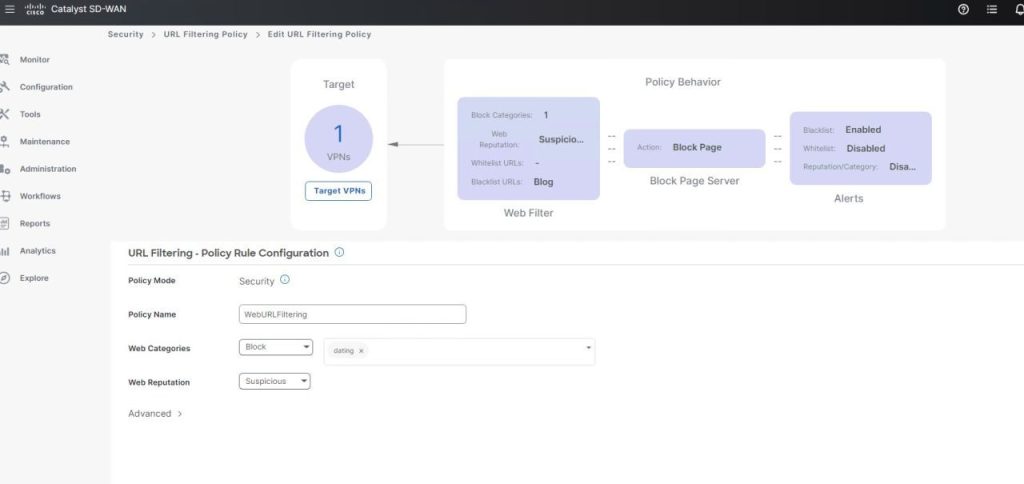
What is it?
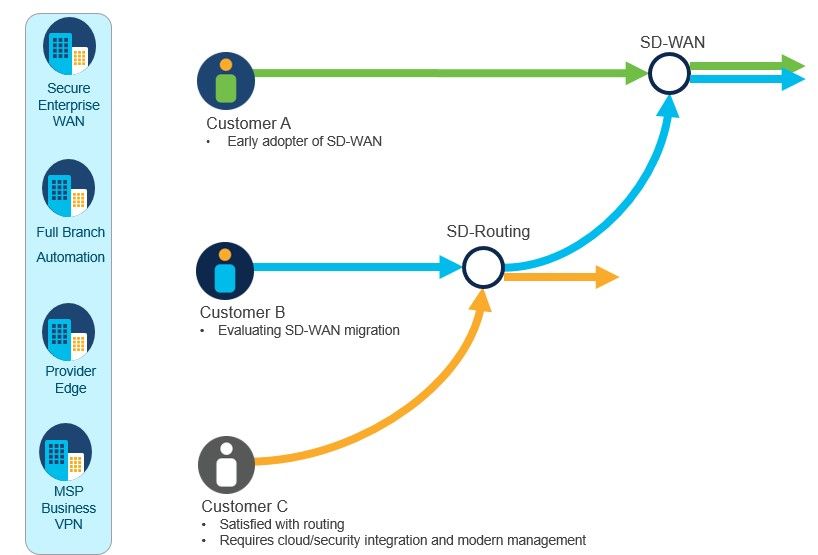
SD-Routing bridges the ‘in between’ from a traditional WAN and SD-WAN. I think of it as in the middle, so you’re not quite ready to jump on the SD-WAN train 🚅 but would like to move on from traditional WAN.
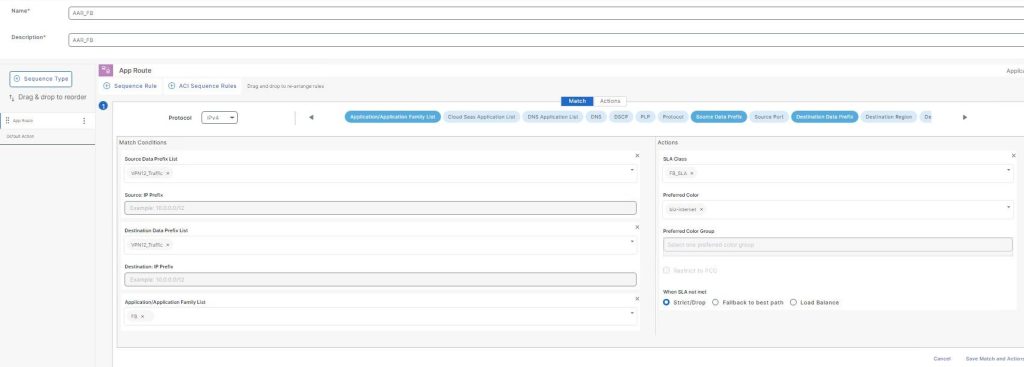
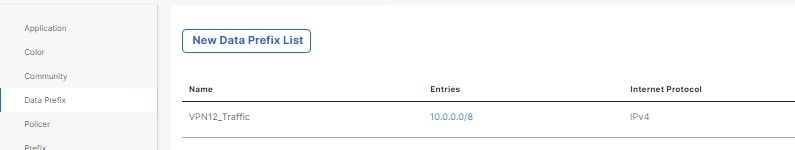
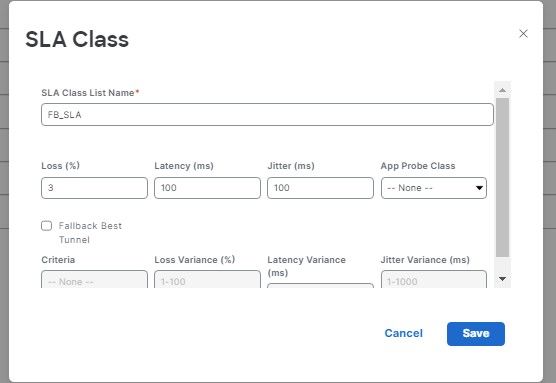
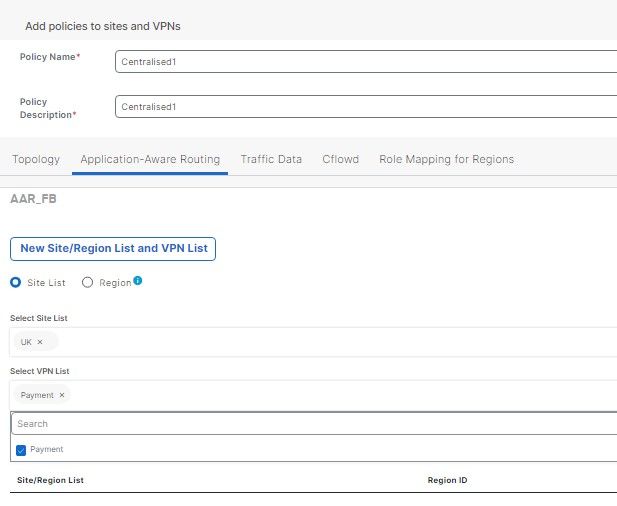
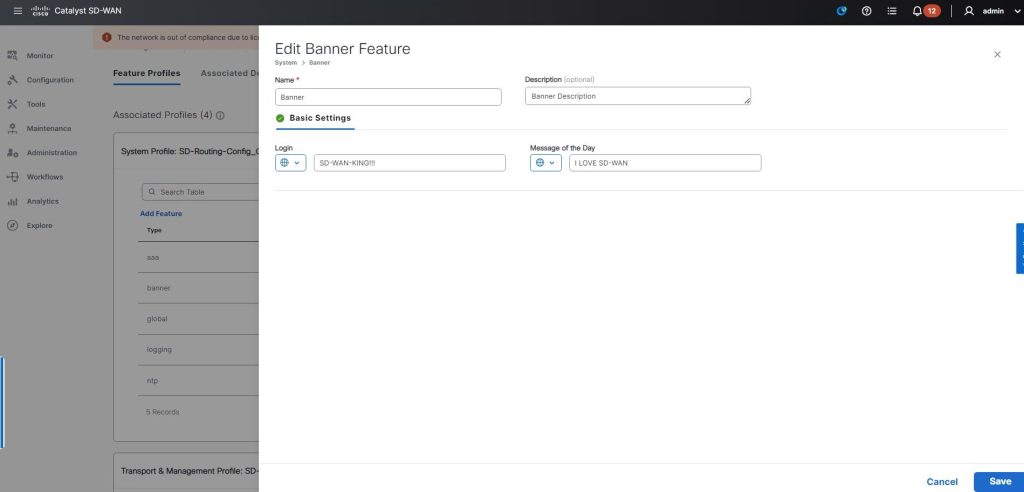
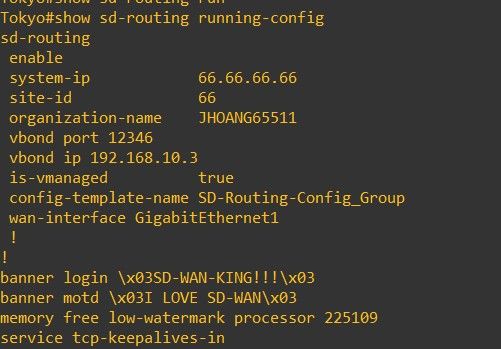
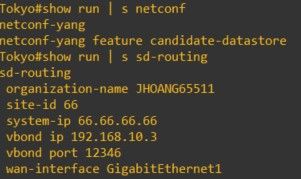
Traditional WANs, you configure devices via CLI, and if you had 20 branches you’d end up with Notepad++. With SD-Routing, you can configure traditional features of a WAN but via GUI (SD-WAN Manager). I learnt the hard way by configuring SD-Routing using v20.13 realising certain features are missing. With v20.14, I can actually configure devices and pushing them out via Configuration-Groups. 🌟
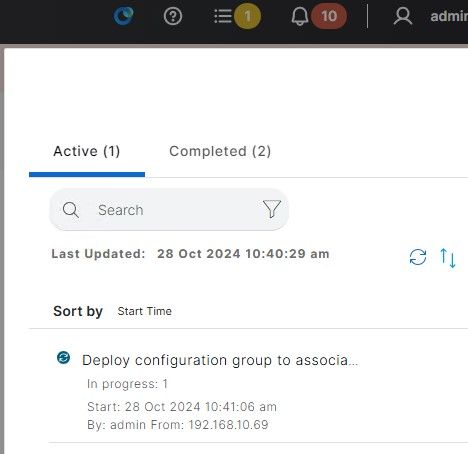
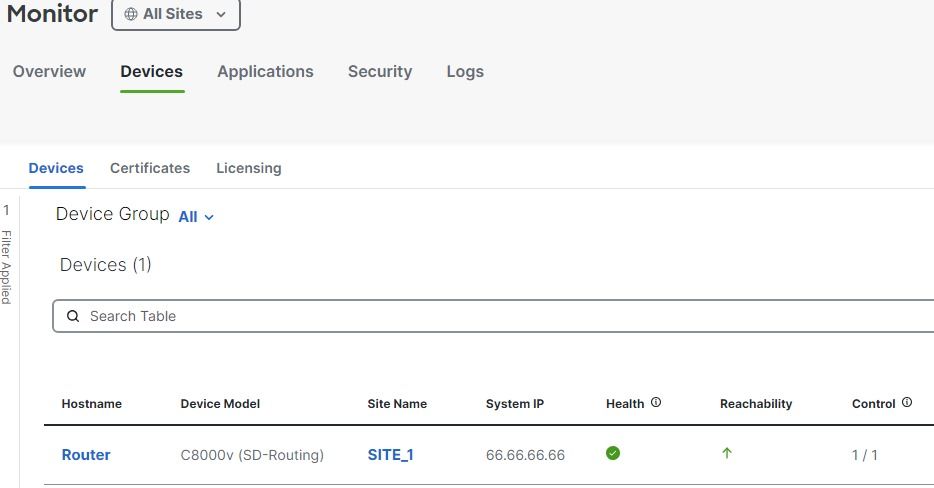
On top of configuration, you can monitor your devices/WAN with SD-Routing.
I have managed to lab SD-Routing and hope to talk about this more in my next/future posts!
This is just a high-level and I have included some slides that illustrate SD-Routing, next post should be demonstrating how to configure SD-Routing. As usual, I hope this helps! 😁