I may have previously touched up on CoR in my previous blogs, but I would like to dedicate a blog post specifically about CoR.
So what is CoR actually?
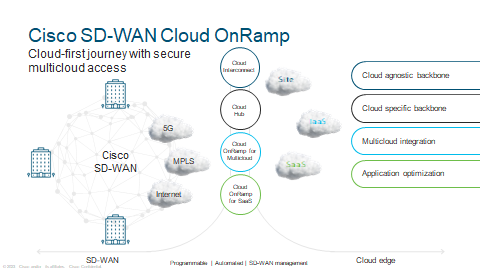
SaaS – Uses real-time, granular analytics for each application to steer users onto the best-performing path for optimal application performance. In another words, best path available to your Cloud environment.
COR for Multicloud –Cloud Hub -Extend the WAN to a public cloud with a single SD-WAN fabric. Apply consistent policy to cloud workloads.
Cloud Interconnect—Automate on-demand connectivity between multiple sites and to leading cloud provider networks, directly from your SD-WAN controller.
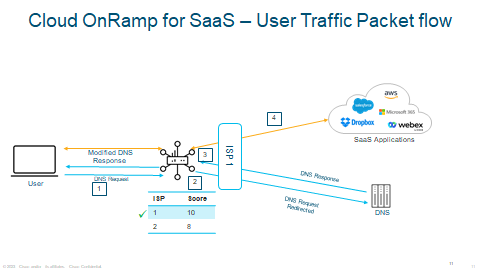
CoR SaaS
1 – All transports that are able to provide SaaS access will request DNS on their Transport VPN 0.
2 – HTTP/S pings are sent to the SaaS provider to begin measurement.
3 – Scores are measured with a best score of 10.
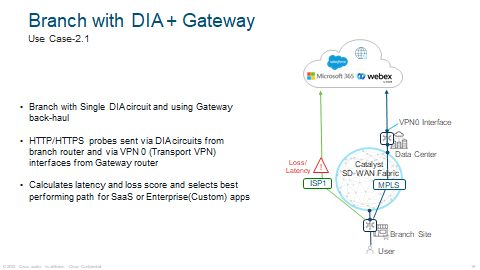
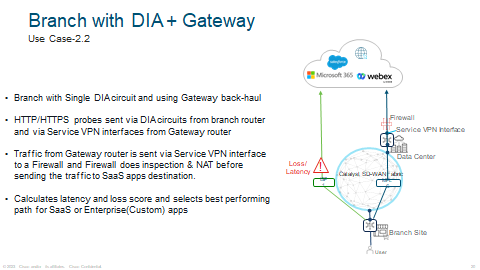
As you can see the example of a CoR traffic flow in how it all works. ISP 1 has the best score therefore it will choose ISP 1.
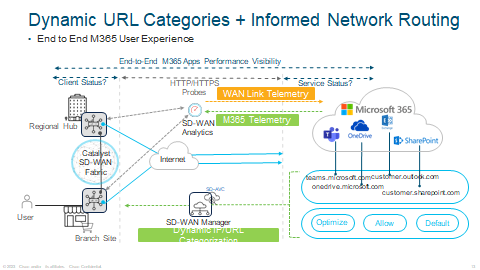
An example of CoR for Microsoft 365, Dynamic URL Categories is where you can multiple Microsoft Service offerings such as Teams, Outlook, Sharepoint etc.
With Informed Network Routing, this is end to end telemetry for the Services I mentioned above, this allows CoR to select the best path depending on the SaaS application with a score.
With CoR, you can also monitor Webex where Edge router will sends HTTPS probes to Cisco Webex Responders across Cisco’s global regions.
Webex API enhances the classification of traffic that needs to go to the best performing Webex region.
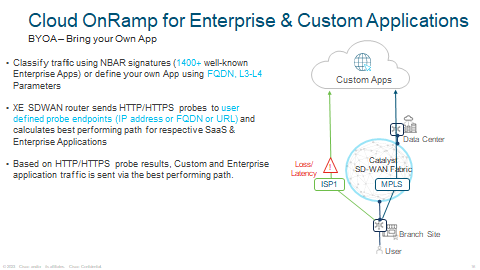
You can even configure and setup your own CoR for your own custom applications usning NBAR or your own FQDN application. Same principle applies with HTTPS probes.
Examples and uses cases of CoR:
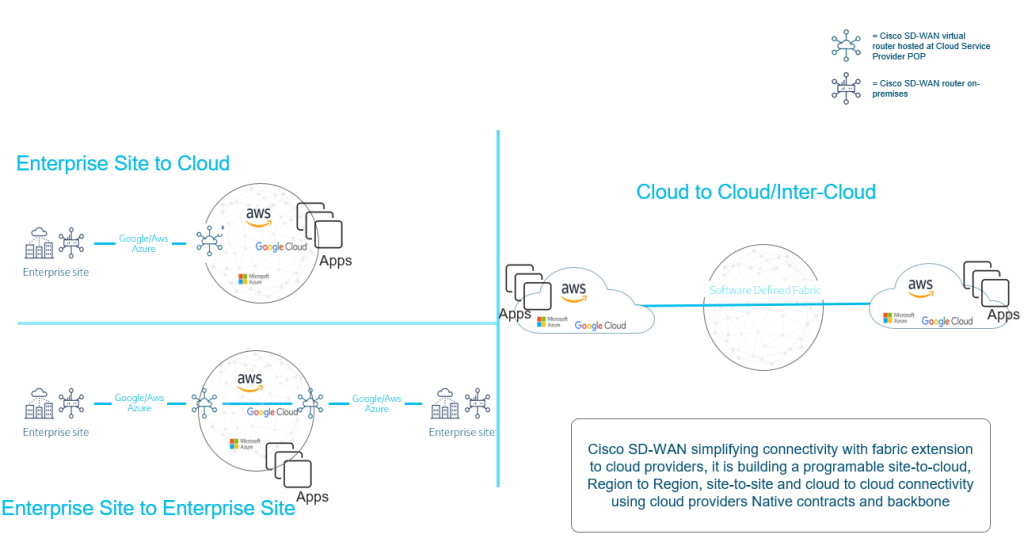
CoR Multicloud
In this model we spin up virtual routers (Cat 8000v) inside the cloud service provider to extend the SDWAN fabric all the way to the application and networking of the CSP. This can be automated by developing workflows in SD-WAN Manager. Workflows is a new tool that helps you click and configure features without the need of defining Groups of Interests like we use to have. This workflow allows the user to configure without the expert knowledge required in the Cloud world. This allows network operators to easily deploy the SDWAN service in each of the cloud service providers. SD-WAN Manager can then deploy and bootstrap the cat8000v in the CSP. Within minutes your SDWAN environment will have access to your key applications running in the CSP.
AWS
There is different use cases when you are spinning up within the AWS environment. Below are a few examples in how you can leverage SD-WAN and AWS.
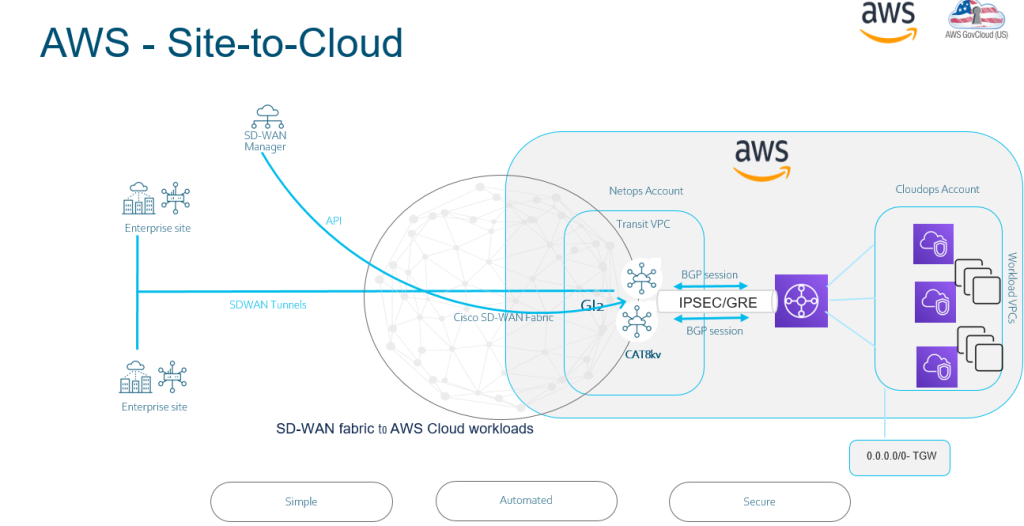
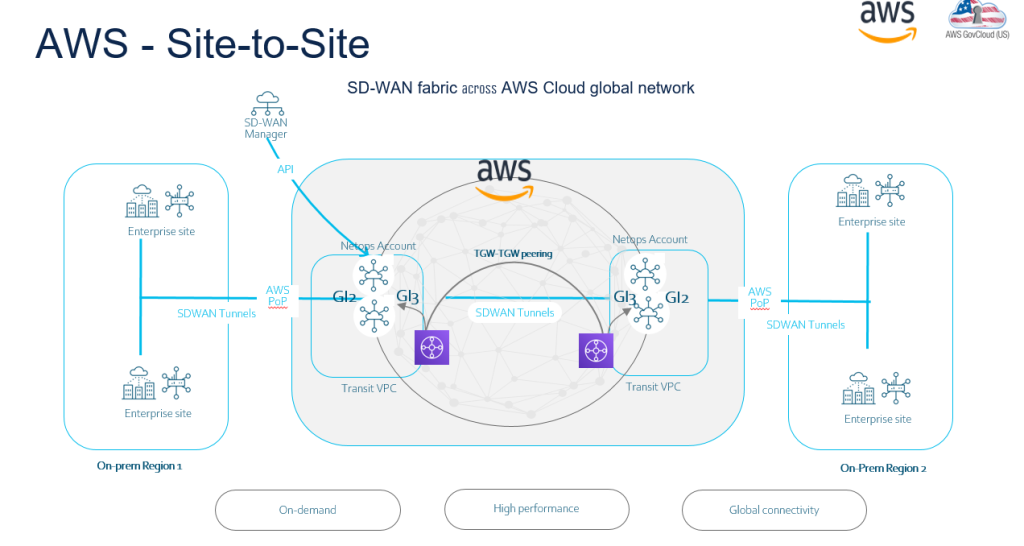
The above example above illustrates where you have a AWS region with Cat 8kv deployed in HA, but you also have another region for example in USA. So to connect between two regions you can spin up Transit Gateway so the SD-WAN fabric can be extended.
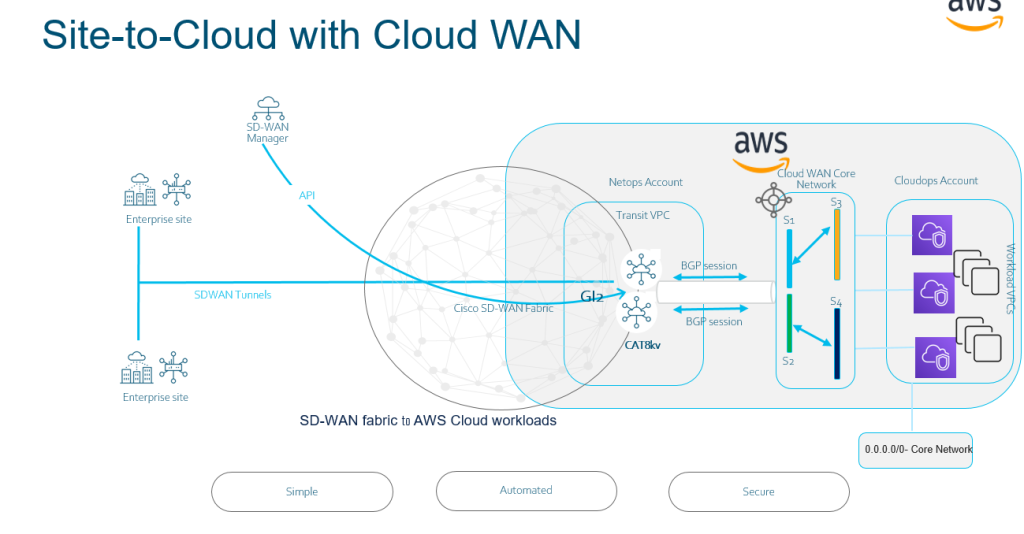
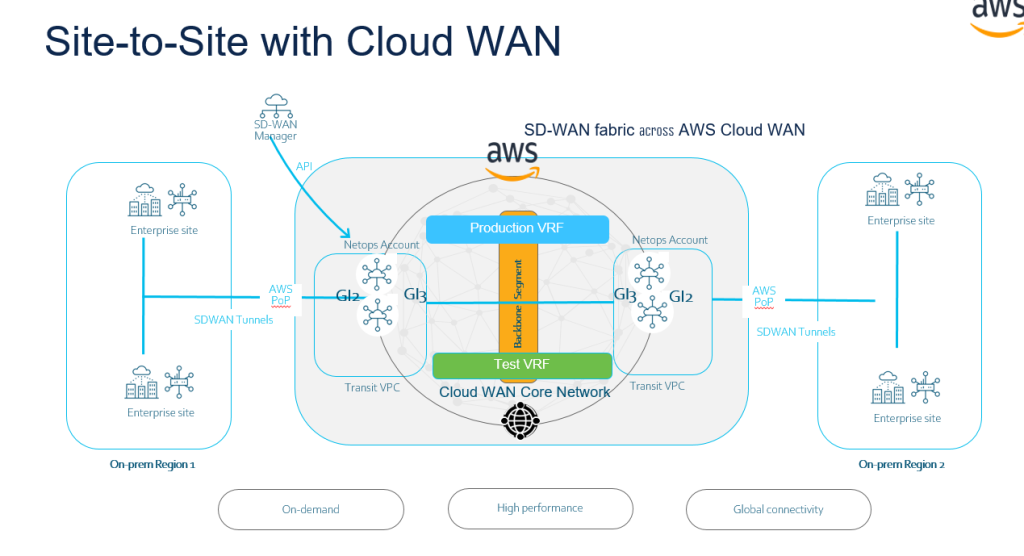
AWS Cloud WAN is a managed wide-area networking (WAN) service that you can use to build, manage, and monitor a unified global network that connects resources running across your cloud and on-premises environments. It provides a central dashboard from which you can connect on-premises branch offices, data centers, and Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) across the AWS global network. You can use simple network policies to centrally configure and automate network management and security tasks, and get a complete view of your global network.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/network-manager/latest/cloudwan/what-is-cloudwan.html
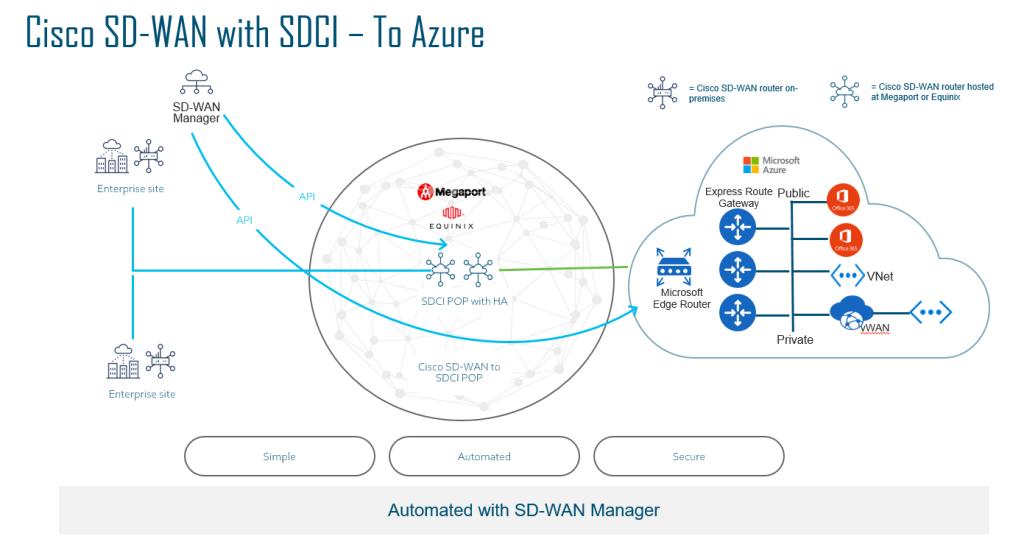
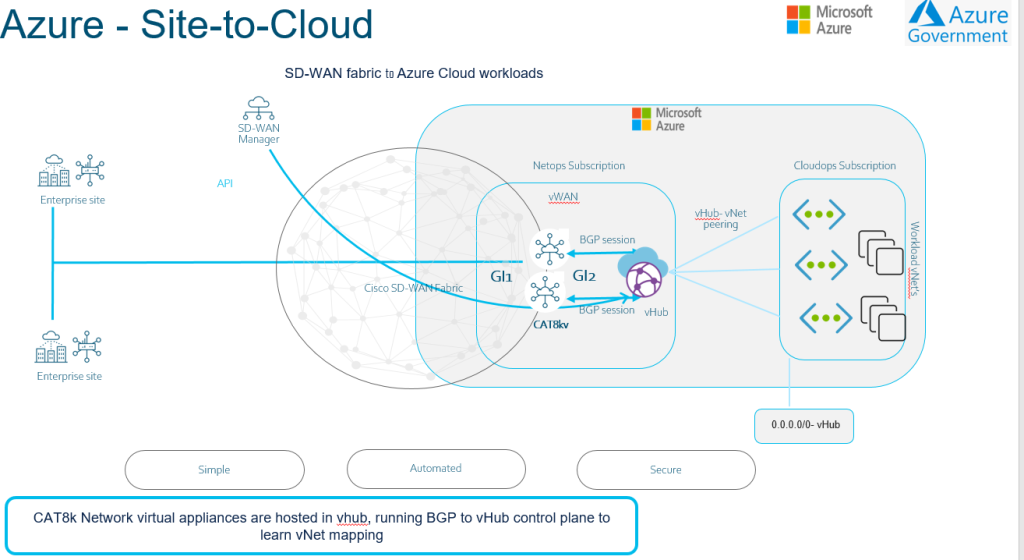
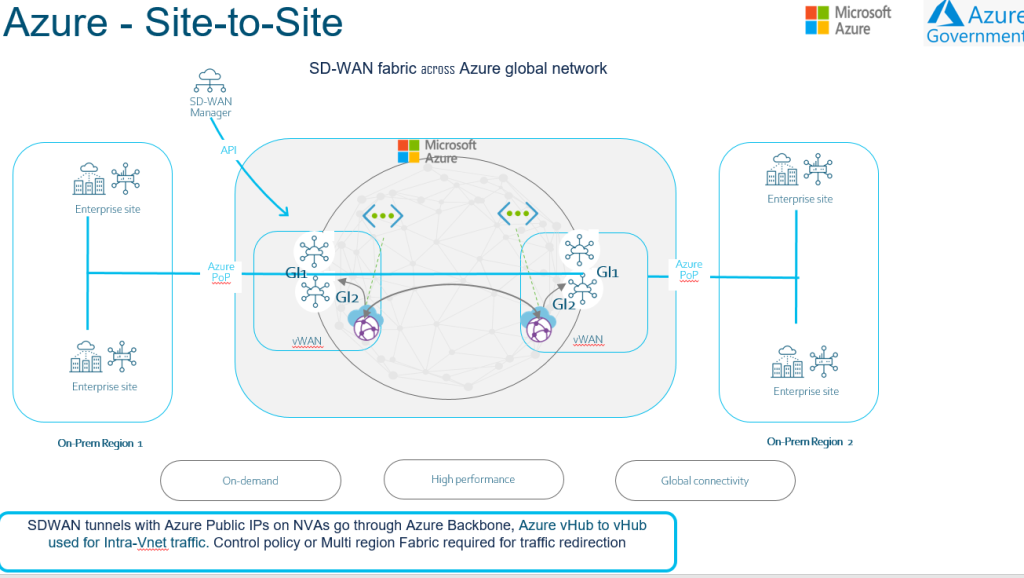
Azure
Multicloud
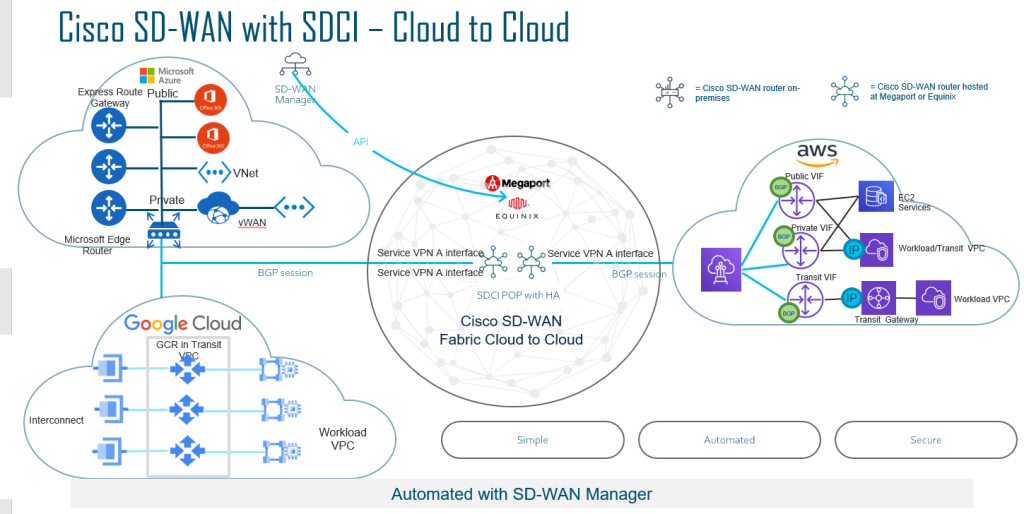
With SD-WAN you can even connect your other Cloud providers with other cloud providers as part of your SD-WAN fabric. The example below basically illustrates if you use AWS for a specific workload and Azure for another Workload.
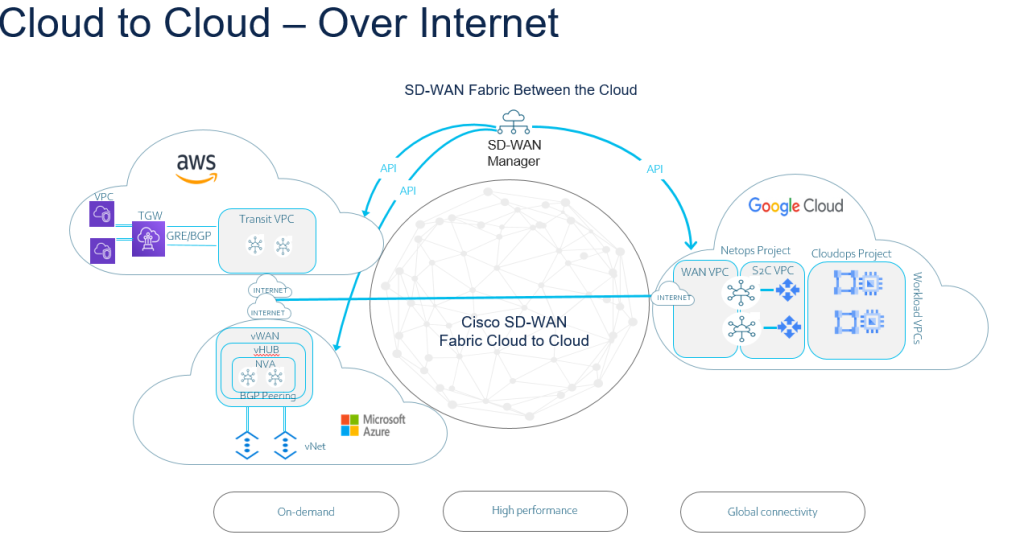
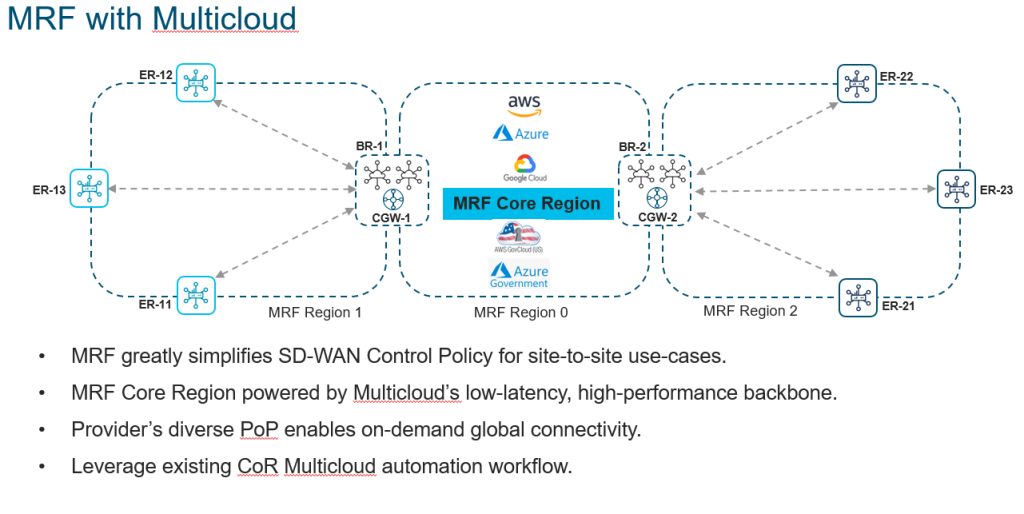
I’ve previously wrote a blog about MRF, but you can even implement Multicloud acting as your Region 0 (Backbone) from a design perspective.
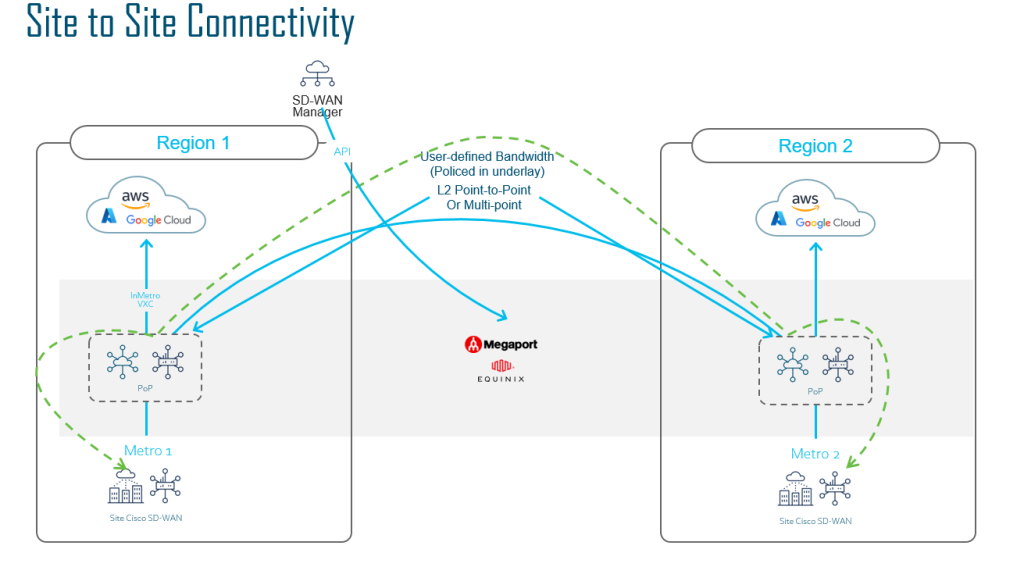
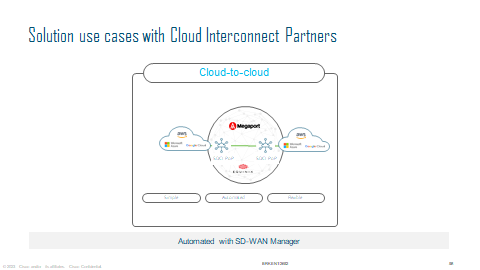
Multicloud Interconnect
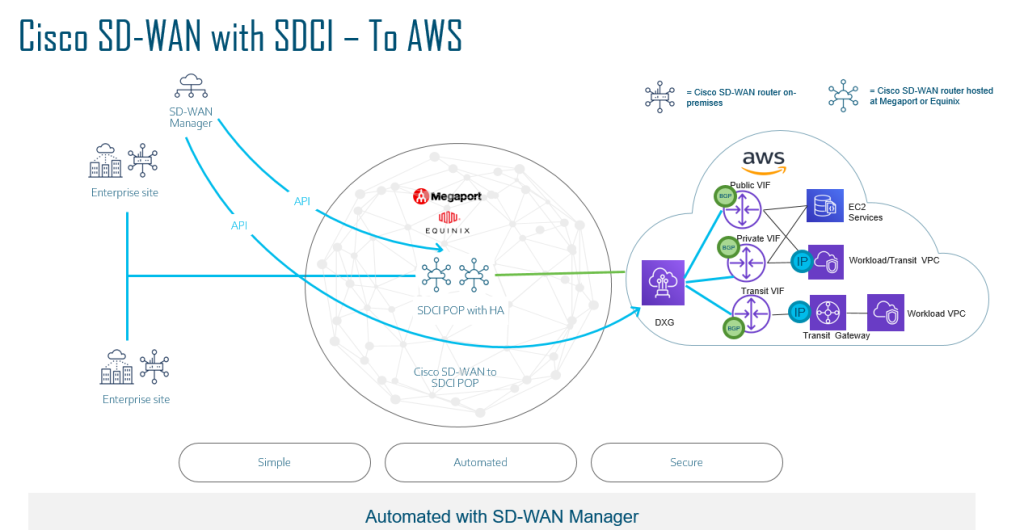
Cisco has partnered with Equinix and Megaport as the backbone provider. Essentially if you wanted a private back bone in your core network, you could utilise either partner and spinning up a Cat 8kv.
So instead of relying on the Internet as your transport for a Cloud to Cloud SD-WAN fabric, you can utilise the high speed backbone to connect back to your Cloud Provider. Most providers will usually build a Private MPLS L3VPN network in order to connect to the cloud provider, using Interconnect providers, you do not need to rely on your local ISP’s to do this.